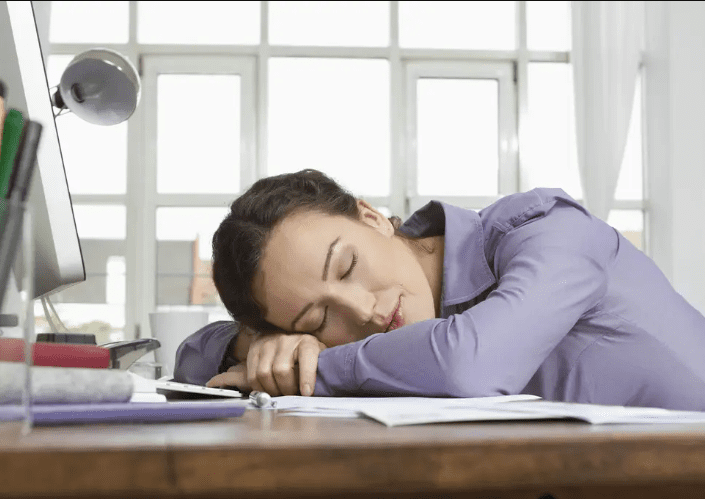
Many companies in Spain have understood this, China and Japan, that give their employees a mid-day nap, while in the United States, Italy, and many other countries, rest in the workplace is seen as a waste of time.
Taking a nap in the afternoon is a good habit. It recharges the mind, the body, and has a positive effect on the economy. Many companies in Spain, China, and Japan have understood this, giving their employees a mid-day nap, while in the United States, Italy, and many other countries, rest at work is seen as a waste of time. But according to the researchers, it is far from a slacker’s habit. Here are the reasons, from several points of view:
Mental: a nap of a maximum of 6 minutes improves long-term memory and increases the ability to remember facts and notions. A 20-30-minute nap improves motor skills (including keystrokes) and alertness, while 30-60 increases decision-making skills. NASA has found that a 40-minute nap improves performance by 34% in military pilots and astronauts.
Physical: The body also benefits from an afternoon nap. Studies have shown that those who indulge in restful sleep have lower levels of cytokines (a high concentration can damage organs) and norepinephrine (which can cause hypertension, anxiety, and tachycardia).
Economic: According to Wilson Quarterly magazine, a 2011 study showed that lack of sleep, and the inevitable exhaustion that comes with it, cost $63.2 billion a year in lost productivity, while the world spends $70 billion on sleep-enhancing products. Other studies show that a quick 20-30 minute nap increases work performance by up to 34% through reduced stress, greater attention to detail, and improved cognitive skills. Naps also lead to less impulsive decisions and greater tolerance to frustration.
Siesta lovers are right, therefore, that, contrary to what is thought, it is not at all linked to doing nothing. According to Juan José Ortega, sleep expert and vice president of the Spanish Sleep Society, the word “siesta” comes from the Latin Sexta: “Romans used to stop to eat and rest at the sixth hour of the day. If we keep in mind that they divided the periods of light into 12 hours, the sixth hour corresponds in Spain to the period between 13:00 and 15:00, depending on the season”.
But how has this practice become so widespread in Spanish culture? “In a word, war,” notes Quartz. “After the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s, many people worked two jobs to support their families. The two-hour break was perfectly located to allow workers to go home and take a short break between shifts, eat a meal, take a nap, and spend time with their families. But today, the habit may be dripping: “60% of Spaniards say they never take a siesta, perhaps because high unemployment drives workers to work as hard as their bosses who work long hours”.
Not everyone, the researchers warn, can indulge in the luxury of a nap: according to Michael Perlis, Assistant Director of the sleep research laboratory at the University of Rochester, those suffering from insomnia or depression “would do better to avoid in order not to worsen the symptoms.”